Software Quality Management (SQM) refers to a comprehensive approach in software development that focuses on ensuring the final product’s high quality. It encompasses a trio of fundamental aspects that QA specialists prioritize: quality assurance, quality control, and product testing.
1. Quality Assurance (QA)
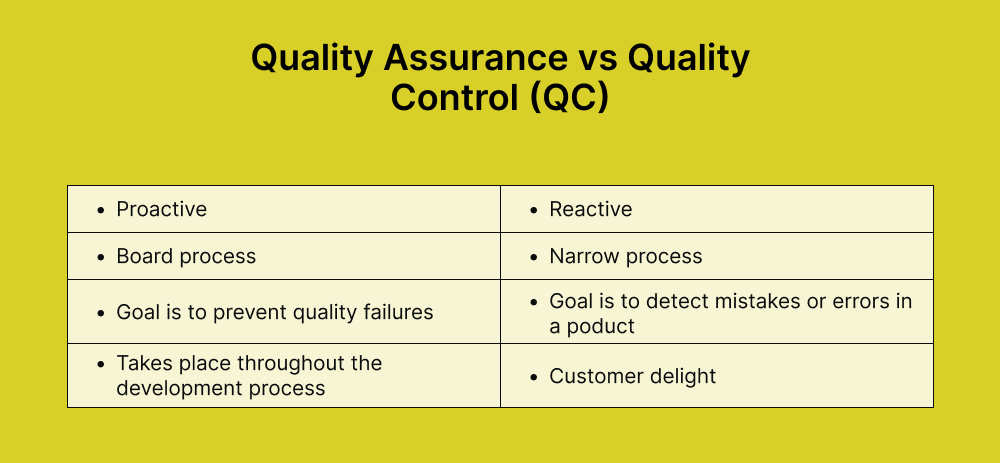
Quality Assurance (QA) involves a set of intentional actions and organizational procedures to ensure that the software development process adheres to established standards. The primary focus of QA is on the methodologies used during development, intending to prevent errors before they occur. Standards under QA are established at the beginning, even before the actual software development process starts.
2. Quality Control (QC)
Quality Control (QC) is a process that focuses on the quality of the software product being developed. It comprises specific tasks and procedures related to a particular project. It aims to ensure that the product meets all specified requirements and standards throughout development. In other words, QC is all about verifying and validating the product against predefined criteria to ensure its quality.
3. Product Testing
This is a key component of SQM and involves identifying and resolving technical issues in the developed software. Product testing is crucial for confirming that the application is stable, user-friendly, performs well, and is secure. While it is deeply integrated into the software development lifecycle, the approach to product testing is influenced by both QC and QA strategies. Product testing is essential in various industries. Here are six key types:
1. Concept Testing
It tests the viability of a product idea. Methods include customer surveys or wireframes. It helps in deciding whether to move forward based on customer feedback. Example: A company surveys customers about a new sugar-free cereal to gauge interest.
2. QA Testing
Conducted in a staged environment to ensure the product works as intended. It involves testing scenarios to mimic customer experiences. Example: A restaurant chain tests a new map feature in their app across different systems before public release.
3. A/B Testing
It involves comparing two versions of a product feature to determine which one customers prefer. It’s useful for design decisions. Example: A retail company tests two color schemes for a website button to see which attracts more clicks.
4. Market Testing
Releasing a product to a select group to gauge market response helps sales forecasting and marketing planning. Example: A clothing store tests a new line of athletic wear with a group of customers to estimate sales.
5. User Testing
Done post-launch to observe how customers use the product. It informs changes in future updates based on user experience. Example: A photo app company conducts a focus group to understand why a new feature is underused.
6. Regression Testing
Performed after the product was used to ensure new updates didn’t affect existing functionalities. Example: A food delivery app is tested for new features to ensure they work without impacting existing functions.